Discover the treasures of ancient Rome in POMEPII: THE EXHIBITION now on display
Thousands of years after its collapse, ancient Rome is well known for its ingenious engineering tactics and advanced technology. From constructing hundreds of roads stretching thousands of miles to maintaining a water supply sustaining millions of people, Roman engineers provided the ancient world with technology ahead of its time.
Here are 5 ways that Roman technology was ahead of its time:
1. “All roads lead to Rome”
“All roads lead to Rome.” This saying was particularly true during the height of the Roman Empire when 50,000 miles worth of roads stemmed from the capital. The people of Rome utilized different engineering techniques to survey, clear and level land suitable for direct paths between cities. Additionally, tunnels and bridges were built along their roads along with paths for pedestrians. Due to the extensive network of roads, military personnel were able to cover ground extremely fast. Citizens could easily travel due to directional signage, and goods were traded efficiently.
The Roman road network was used as a tool to help conquer and hold onto a vast amount of land, and the engineering techniques utilized by the Romans have been used as a basis for many modern roads throughout Europe.
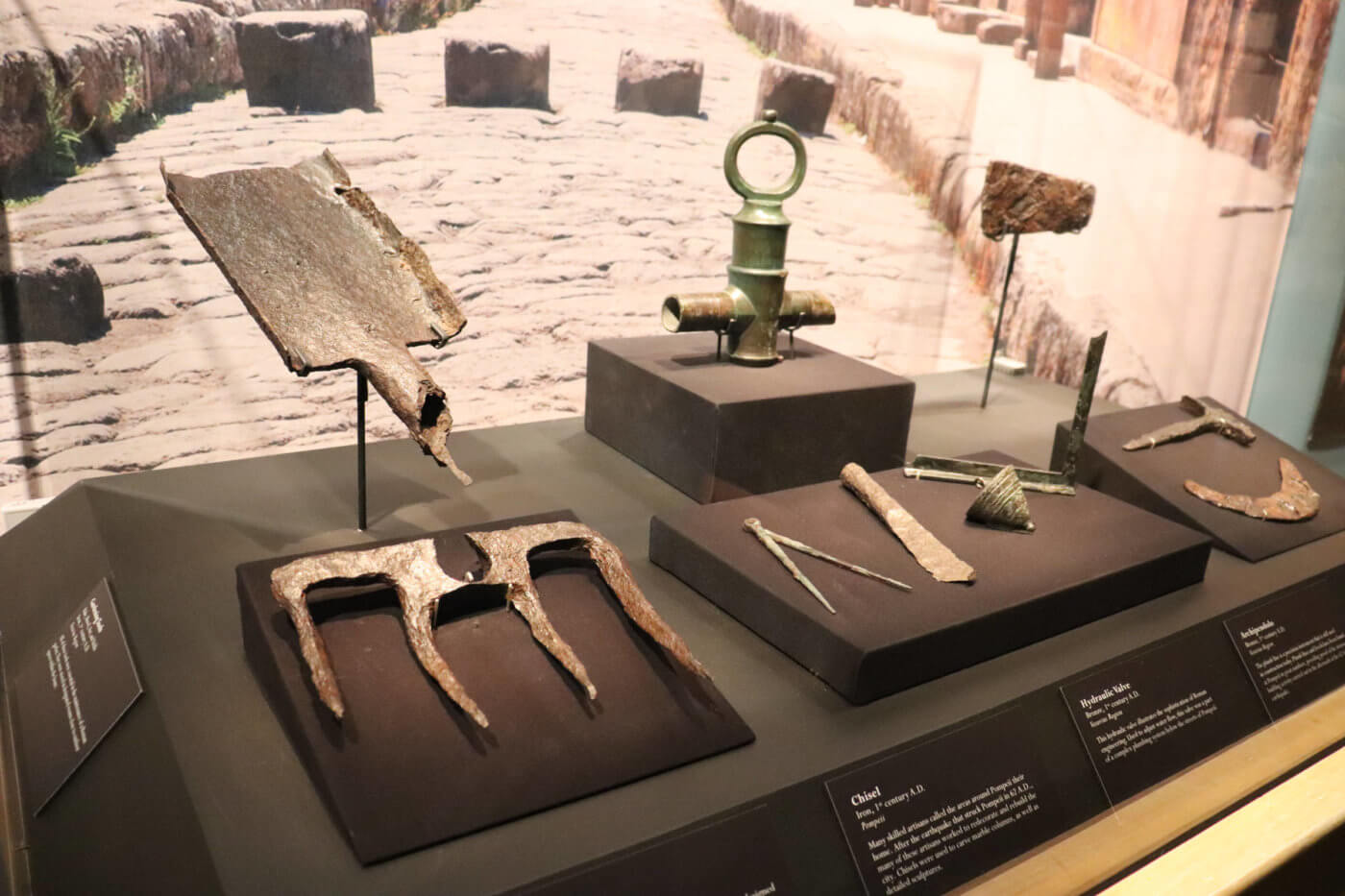

The Romans revolutionized running water with their aqueducts. The capital city of Rome had 11 aqueducts supplying water to its citizens. This water supply not only assisted in sustaining an enormous population but also made public hygiene and sanitation possible.
Roman aqueducts were designed to approach the city at a deteriorating angle, called a gradient. The slope of these aqueducts had to be calculated from a very high distance with some reaching up to 60 miles long, and they had to be executed perfectly regardless of the terrain. For this to be possible, Roman engineers dug tunnels through mountains in higher terrain and crafted stone walls for the pipes to run through deeper land.
Once the water supply reached a city, it would be transferred to various holding tanks that supplied citizens with drinking water, public bathing water and the wealthy with private water supplies. The famous Trevi Fountain of Rome uses water from one of the restored aqueducts of the ancient city.
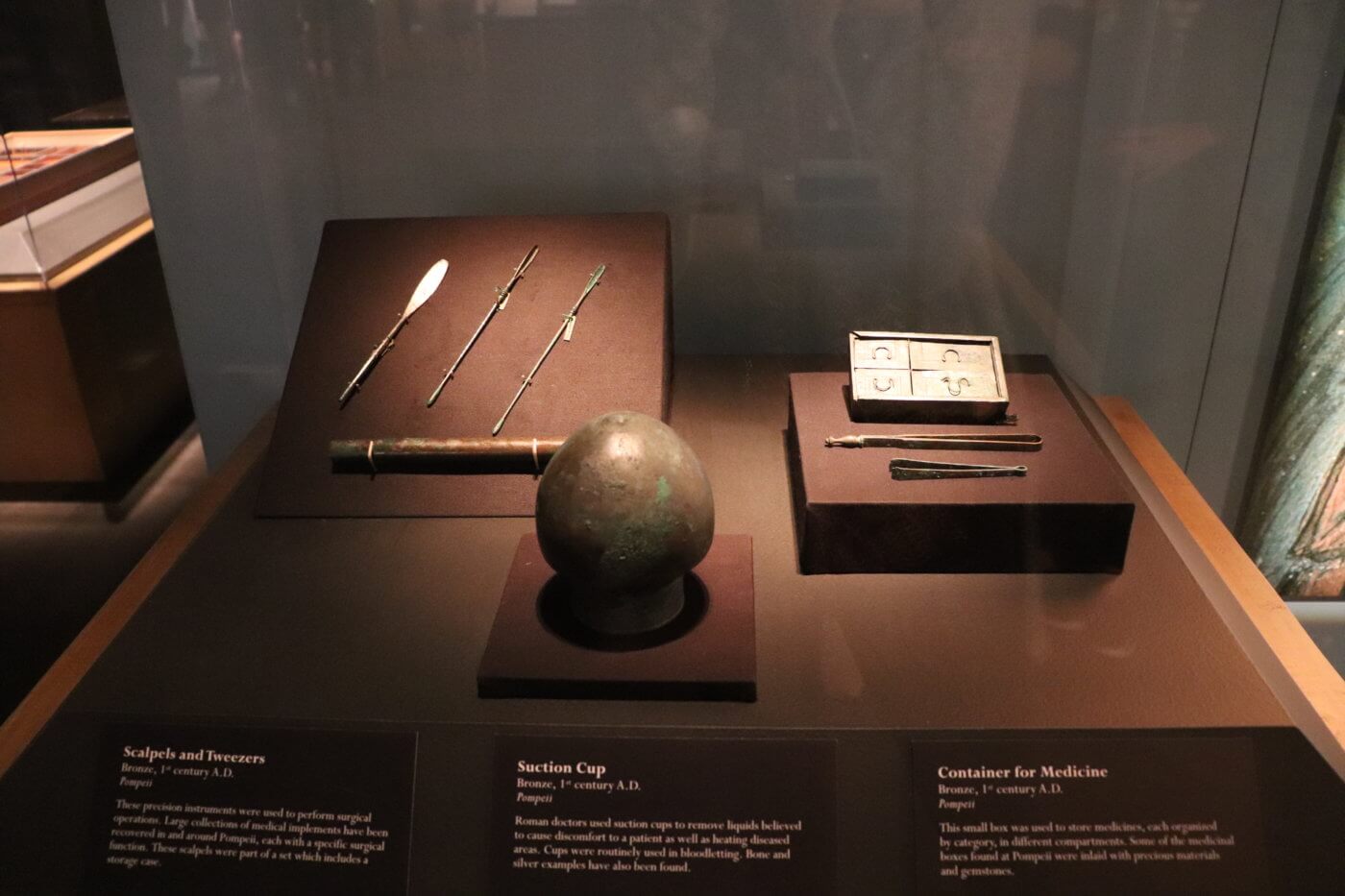
3. Battlefield medicine
Despite the risk of being harmed at war, soldiers of ancient Rome often lived longer than the average citizen. This is due to the medical advancements of their time, specifically in battlefield treatment.
Roman field doctors contributed to the increased sanitation of military camps and performed physicals on new soldiers. Field surgeons utilized arterial surgical clamps and tourniquets to slow blood loss in battle wounds. In ancient Rome, the battlefield was the best place for surgeons to get experience, and the doctors of the military proved to be among the best of their time.

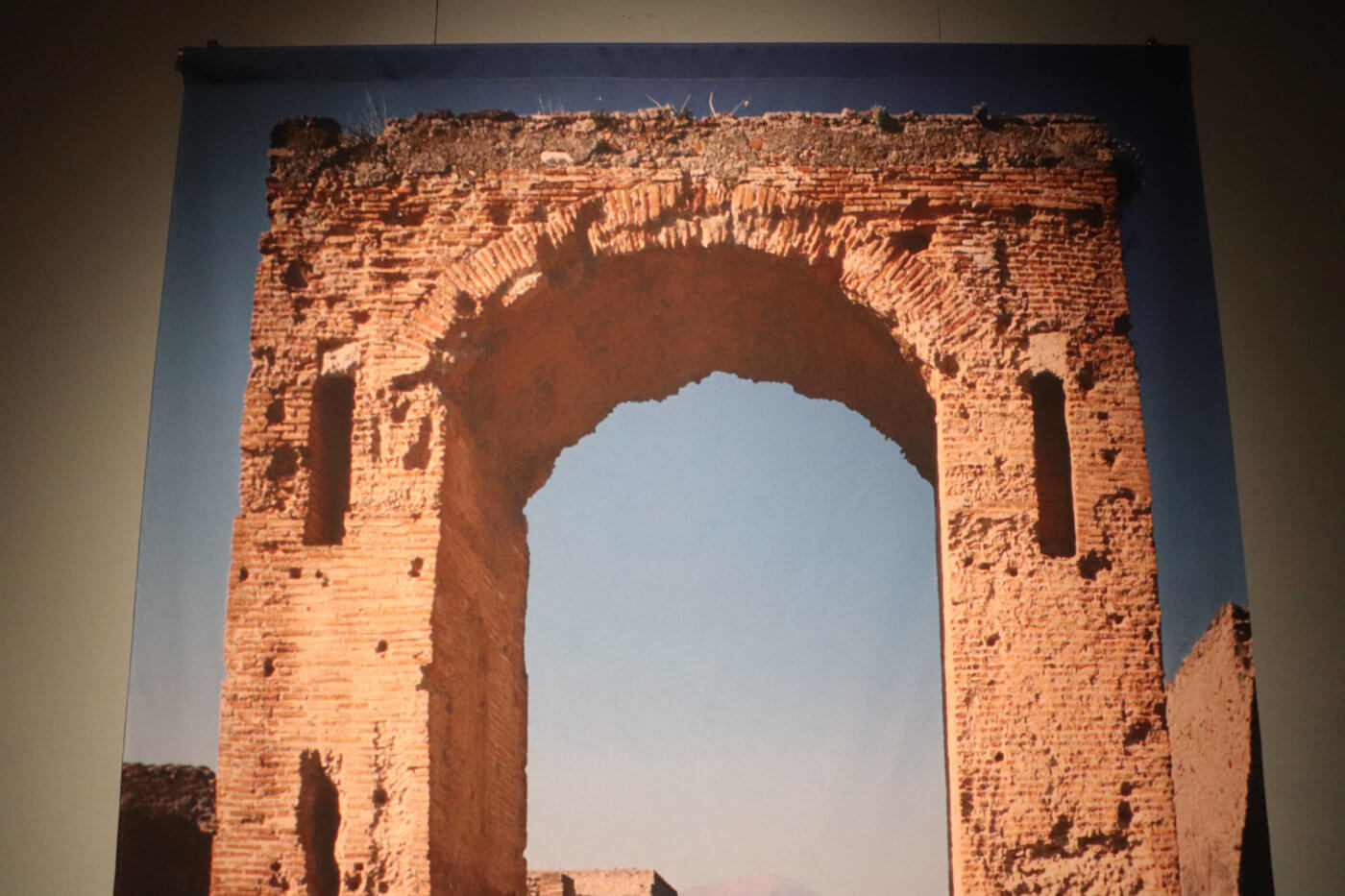
Although arches existed thousands of years before the time of ancient Rome, the Romans revolutionized the structure by using it to build colosseums, aqueducts, bridges and other buildings.
Roman engineers created wooden frames in the shape of an arch, then created the stonework around the frame. The centermost stone at the top of an arch is called a keystone, and the wooden frame was removed once the keystone was put in place. Weight is transferred from the keystone through the other stone wedges of the arch’s external frame, creating a strong tool that Roman architects utilized in their buildings and monuments.

Roman concrete has passed the test of time. By using lime and volcanic rock, the Romans were able to create a magnificent mortar that can still be seen thousands of years later.
Roman concrete was revolutionary in ancient architecture for a few reasons. Firstly, concrete is very flexible when poured into molding layers and takes the shape of its container. Second, it did not require much skill to pour concrete into molds in comparison to cutting stone for the base of buildings, making concrete much cheaper. Lastly, concrete was simply stronger and more time efficient compared to previous building methods used in the ancient world.

Much of what is known about the ancient Rome comes from Pompeii, a Roman city frozen in time by Mount Vesuvius’ eruption in 79 AD. Visit POMPEII: THE EXHIBITION to learn more about Roman technology while exploring the ancient city of Pompeii.